The terms heartburn, acid reflux, and GERD are often used interchangeably. They actually have very different meanings.
- Acid reflux is a common medical condition that can range in severity from mild to serious.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is the chronic, more severe form of acid reflux.
- Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD.
What is acid reflux?
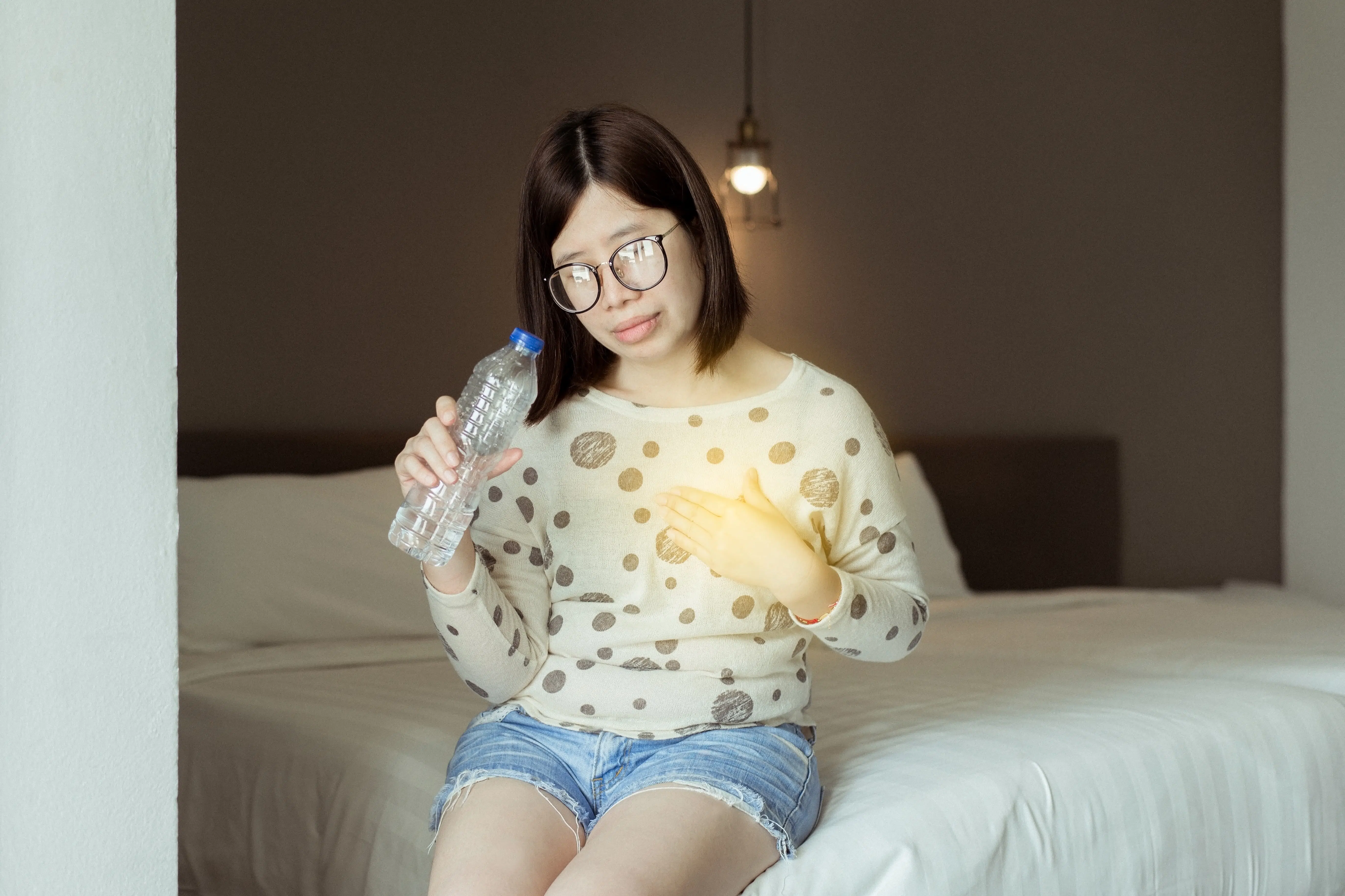
A circular muscle called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) joins your esophagus and stomach. This muscle is in charge of tightening your esophagus after food passes to the stomach. If this muscle is weak or doesn’t tighten properly, the acid from your stomach can move backward into your esophagus. This is known as acid reflux.
Acid reflux can cause heartburn and other symptoms that include:
- cough
- sore throat
- bitter taste in the back of the throat
- sour taste in the mouth
- burning and pressure that can extend up the breastbone
GERD in children
From babies to teenagers, children of all ages can experience GERD. About one-fourth of all children and teenagers experience symptoms of GERD.
The condition is especially common in infants because their stomachs are much smaller and less able to tolerate being full. As a result, stomach contents can easily come back up.
Symptoms associated with GERD in infants include:
- being especially irritable or inconsolable after a feeding
- choking
- forceful regurgitation, especially after burping
- fussing, especially after a feeding
- not gaining weight at a normal rate
- refusing to eat
- spitting up
- vomiting
- wheezing
- breathing difficulties
About 70 to 85 percent of infants have regurgitation the first two months of life. Typically, 95 percent will outgrow the symptoms by the time they reach 1 year of age. Children with developmental and neurological conditions, such as cerebral palsy, may experience reflux and GERD for longer time periods.
It’s important doctors diagnose GERD in children early to lessen the likelihood they’ll have complications.
As a child ages, they can still experience symptoms of GERD. The symptoms include:
- bad breath
- chest discomfort
- frequent respiratory infections
- heartburn
- hoarse voice
- abdominal discomfort
Talk to your child’s pediatrician if you think your child is experiencing GERD. Untreated symptoms can cause permanent esophagus damage.
Contact Us:
If you have been searching Google for a gastroenterologist near me, gastroenterologist for children near me or children’s gastroenterologist near me, look no further then Gainesville Pediatric GI. Schedule a consultation online at gastrohealthforkids.com